Understanding Insurance in India: A Complete Guide for Everyone
- Editor

- Aug 22
- 4 min read
by KarNivesh | 22 August, 2025
Insurance in India has evolved from being a privilege of the few to a financial necessity for millions. Today, it is one of the fastest-growing industries in the country, with the market projected to reach ₹19,30,290 crore by FY26, growing at a healthy 7.1% annually. With rising awareness, government initiatives, and digital innovations, understanding how insurance works is crucial for making smart financial decisions.
This guide will break down the essentials of insurance in India its types, benefits, claim process, and future trends in simple language that anyone can follow.

India’s Insurance Landscape: Growth and Potential
India’s insurance penetration (insurance premiums as a % of GDP) touched 3.7% of GDP in FY24 life insurance at 2.8% and non-life at 1.0%. While this reflects steady progress, it still lags behind global averages, showing immense scope for expansion.
Insurance density (premium per person) in India was about ₹8,294 in 2023, compared to the global average of nearly ₹77,600. Clearly, the Indian market still has a vast untapped potential.
Life insurance premiums alone crossed ₹8.3 lakh crore in FY24, marking a 6.1% growth from the previous year. Alongside, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has introduced reforms like reducing waiting periods for pre-existing diseases from four to three years and removing age restrictions in health insurance making policies more consumer-friendly.
What is Insurance and Why Does it Matter?
Insurance is essentially a financial safety net. By paying a fixed premium, individuals transfer the risk of large, unexpected losses to the insurance company. In return, the insurer compensates for specific damages or events, such as accidents, illnesses, or death.
The system works on risk pooling many contribute small amounts to create a large fund, which helps those who face actual losses. The key principles include:
Utmost good faith – honesty and disclosure by both parties
Insurable interest – you must have a financial stake in what is insured
Indemnity – compensation for actual loss, not profit
Subrogation – insurer can recover costs from third parties responsible for damage
Types of Insurance in India
The insurance sector is broadly divided into life insurance and general insurance, each offering multiple products.
1. Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection to your family in the event of your untimely death.
Term Insurance: Pure protection plans with low premiums. A policy can cost between ₹8,000–₹15,000 annually for large coverage. It only pays death benefits.
Endowment Policies: Combine protection with savings. Annual premiums range from ₹20,000–₹40,000 and also provide maturity benefits.
ULIPs (Unit Linked Insurance Plans): Market-linked policies investing in equity and debt. Suitable for those comfortable with investment risks.
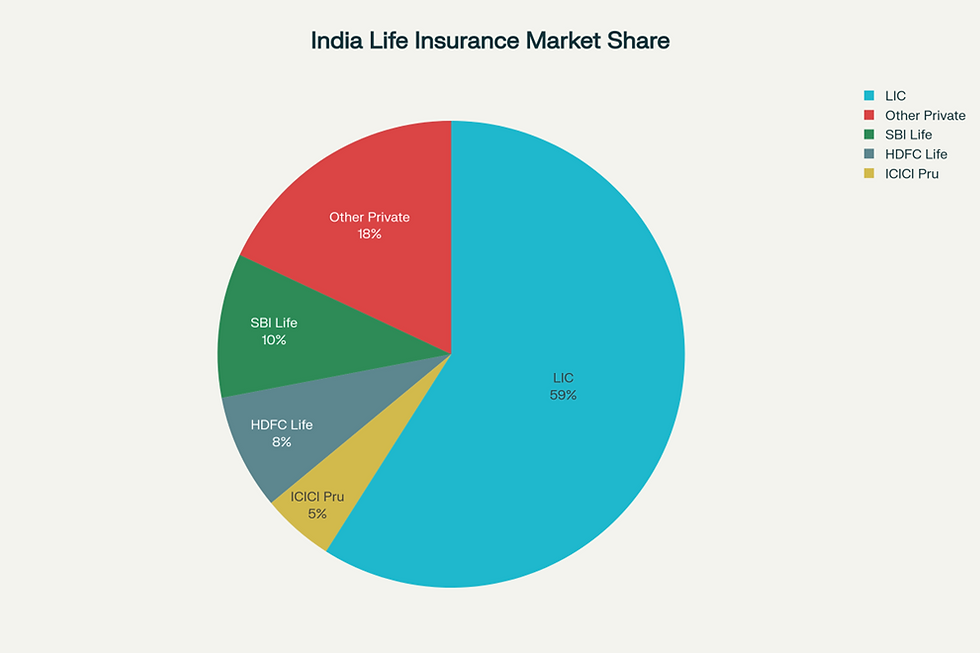
LIC dominates with nearly 59% market share, followed by SBI Life (10%), HDFC Life (8%), and ICICI Prudential (5%).
2. General Insurance
General insurance covers health, vehicles, property, and travel.
Health Insurance: Annual premiums range from ₹5,000–₹20,000 for individuals, and ₹10,000–₹50,000 for family floaters. This is one of the fastest-growing segments.
Motor Insurance: Mandatory in India. Third-party cover costs about ₹2,000–₹5,000 annually, while comprehensive cover ranges from ₹15,000–₹35,000.
Home Insurance: Annual premiums of ₹5,000–₹15,000 protect against fire, theft, and disasters.
Travel Insurance: Costs between ₹300–₹2,000 annually, covering medical emergencies, baggage loss, and trip cancellations.
Tax Benefits of Insurance
Insurance also doubles as a tax-saving tool under the Income Tax Act:
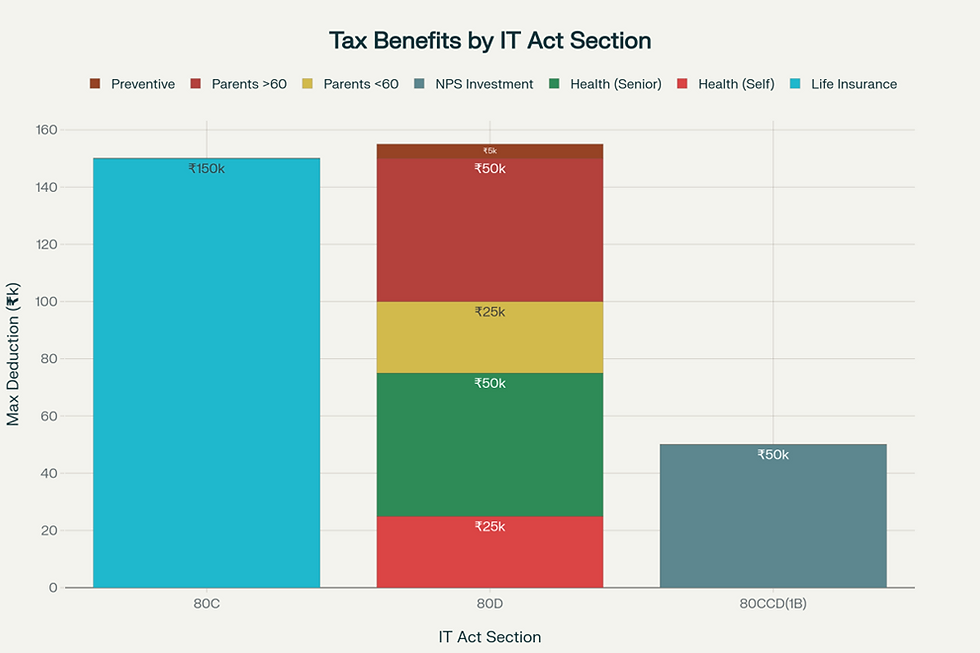
Section 80C: Deduction up to ₹1.5 lakh for life insurance premiums.
Section 80D: Deduction up to ₹25,000 for health insurance (₹50,000 if covering senior citizens).
Section 10(10D): Maturity and death benefits are tax-free under specified conditions.
These provisions make insurance both a protective and wealth-optimizing instrument.
Government Schemes: Insurance for All
To ensure broader coverage, the government runs several schemes, the biggest being Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY).
Provides ₹5 lakh annual health coverage to over 50 crore people.
Covers pre-existing diseases from day one.
Works on a cashless model at over 27,000 hospitals.
Recently extended to all citizens above 70 years.
Such initiatives reduce out-of-pocket healthcare costs and bring financial protection to vulnerable groups.
Digital Transformation and Future Trends
Technology is reshaping insurance in India:
Bima Sugam – IRDAI’s upcoming all-in-one digital marketplace.
AI & Machine Learning – enabling faster underwriting and claim settlement.
IoT Devices – driving usage-based motor insurance.
Insurtech Startups – offering digital-only policies targeting young, tech-savvy customers.
This digital push will deepen penetration and make insurance more accessible.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite growth, challenges remain:
Low awareness in rural areas.
Rising climate risks, making coverage more expensive.
Regulatory compliance costs that smaller companies struggle with.
However, these challenges open doors for innovation. With a large uninsured population, rising incomes, and supportive reforms, the Indian insurance sector is set for massive expansion.
Insurance is no longer optional it’s a cornerstone of financial security. From protecting families with life cover to safeguarding health and assets, insurance plays a vital role in reducing risks.
With supportive regulations, government-backed schemes, and rapid digital adoption, India is on track to achieve its ambitious goal of “Insurance for All by 2047.” For individuals, the key is to stay informed, compare products, and select policies that balance protection with affordability.
In a world full of uncertainties, insurance is the shield that ensures peace of mind and financial stability.




Comments