Open Finance & Embedded Finance: The Future of Digital Banking is Here
- Editor

- Sep 11
- 5 min read
by KarNivesh | 11 September, 2025
The world of financial services is undergoing a dramatic transformation that is reshaping how we interact with money, make payments, and access financial services. Two revolutionary trends - Open Finance and Embedded Finance - are leading this digital revolution, creating unprecedented opportunities for consumers, businesses, and financial institutions. These innovations represent more than just technological upgrades; they are fundamentally reimagining the entire financial ecosystem by making financial services more accessible, personalized, and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.
Open Finance represents the next evolutionary step beyond traditional open banking, expanding the concept of secure data sharing from basic banking information to encompass a comprehensive 360-degree financial footprint. While open banking traditionally focused on payment accounts and transaction data, open finance extends this framework to include insurance policies, investment portfolios, pension accounts, mortgages, and other financial products. The fundamental principle is simple yet powerful: your financial data belongs to you, and you should have control to share it securely with authorized third-party providers to access better financial services and products. This consumer-centric approach operates through secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that facilitate standardized, encrypted data exchange between financial institutions and authorized third-party providers.

The regulatory environment for open finance is rapidly evolving worldwide. In the United States, Section 1033 of the Dodd-Frank Act requires banks to share customer data in standardized formats with authorized third parties, with the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau proposing Personal Financial Data Rights rules beginning implementation in 2025. In Europe, the Third Payment Services Directive (PSD3) aims to create a more secure, efficient, and unified financial ecosystem, while the UK's Financial Conduct Authority conducted an Open Finance Sprint in March 2025, bringing together over 110 stakeholders to develop practical use cases for financial wellbeing and growth.
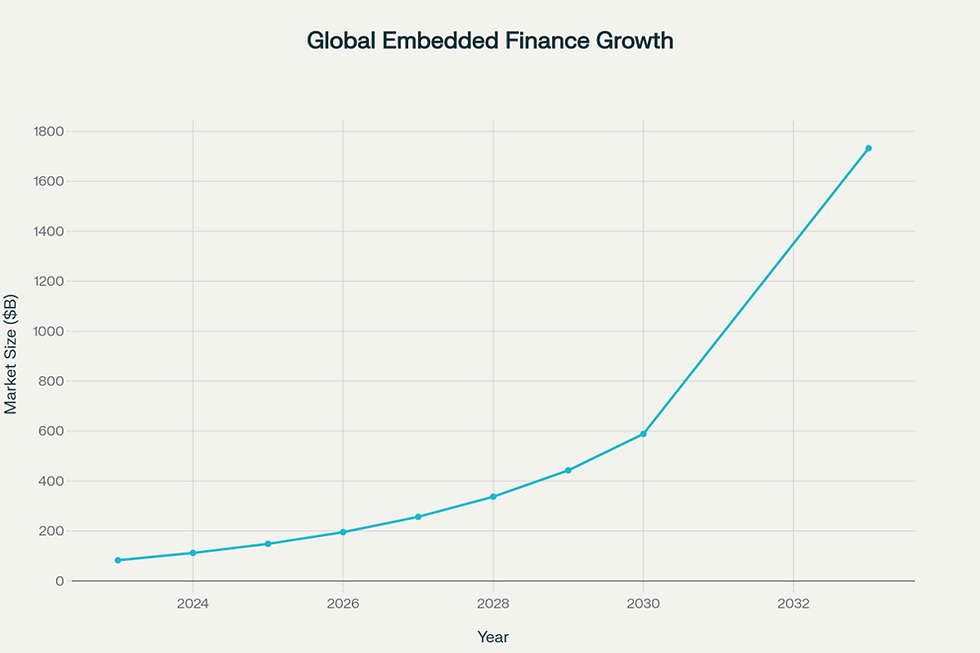
Embedded Finance refers to the seamless integration of financial services and products into non-financial platforms and applications, allowing users to access banking, lending, insurance, and payment services within their existing digital experiences. Rather than visiting separate financial institutions or downloading dedicated banking apps, consumers can access these services directly within e-commerce platforms, ride-sharing apps, social media platforms, and other everyday digital touchpoints. This market is experiencing explosive growth globally, valued at approximately ₹7.29 trillion (USD 82.7 billion) in 2023 and projected to reach an astounding ₹152.8 trillion (USD 1.73 trillion) by 2033, representing a compound annual growth rate of over 30%.

In India specifically, the embedded finance sector has demonstrated exceptional growth, expanding at a 45% compound annual growth rate and expected to reach ₹1.86 trillion (USD 21.1 billion) by 2029. The Indian market is particularly well-positioned for this growth due to its robust digital infrastructure provided by India Stack, including the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Aadhaar biometric identification system, e-sign capabilities, and the Account Aggregator framework. This comprehensive digital public infrastructure has enabled India to become a global leader in digital finance innovation.
India's remarkable success in digital finance stems from this comprehensive digital public infrastructure. The UPI system alone processed over ₹13 trillion in transaction value during recent periods, accounting for 75% of retail digital transactions. With over 600 million smartphone users and 759 million internet users, India has the digital infrastructure necessary for widespread adoption of embedded finance solutions. The Reserve Bank of India has created frameworks that encourage innovation while maintaining security and consumer protection, supporting the country's vibrant fintech ecosystem.
Real-world applications of embedded finance are already transforming the financial landscape. Global examples include Klarna partnering with Worldpay to offer flexible payment options to merchants, and Brazilian neobank Nubank reporting over 45 million consents for financial data sharing, helping users save over ₹102.3 million (USD 1.16 million) through overdraft-alert tools and enhanced credit assessments. In India, successful implementations include the Amazon Pay-ICICI Bank credit card partnership, which accounts for nearly one-third of ICICI's entire credit card user base, and HDFC Bank's partnership with Ola for seamless ride-hailing payments and vehicle financing solutions.
The technology behind both open finance and embedded finance relies heavily on robust API infrastructure that enables secure, standardized communication between different financial systems. These APIs facilitate real-time data exchange, modular integration allowing businesses to integrate specific financial services as needed, and scalability to handle millions of transactions and growing user bases. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are becoming increasingly important, enabling hyper-personalized services through user data analysis, fraud detection using advanced algorithms, predictive analytics helping users make informed financial decisions, and automated financial management through AI assistants.
Security remains paramount in these implementations, with advanced encryption and tokenization protecting sensitive financial data during transmission and storage. Granular consent mechanisms give users control over their data sharing preferences, while adherence to strict regulatory standards ensures consumer protection and system reliability. These comprehensive security measures are essential for building and maintaining user confidence in data sharing mechanisms.
The evolution of open finance and embedded finance is creating numerous market opportunities across different sectors. The retail and e-commerce sector accounts for 39% of the embedded finance market, leading in Buy-Now-Pay-Later adoption and integrated payment solutions. Healthcare applications include embedded insurance and payment solutions that streamline medical billing and coverage verification. Transportation and logistics benefit from integrated financing for vehicle purchases, cargo protection insurance, and seamless payment solutions. Even agriculture is benefiting, with AgriTech platforms providing embedded credit lines and insurance products for farmers.
Looking ahead, market projections indicate continued exponential growth, with embedded finance potentially reaching ₹635 trillion globally by 2030. Technology evolution will include blockchain integration as decentralized finance solutions become more mainstream, Internet of Things devices enabling new forms of embedded financial services, and AI-powered voice assistants managing financial transactions and accounts. As markets mature, we can expect consolidation as larger players acquire successful fintech companies, specialization in developing niche solutions for specific industries, and global standardization through international cooperation on technical standards and regulatory frameworks.
Open Finance and Embedded Finance represent more than just technological innovations; they embody a fundamental shift toward a more inclusive, efficient, and consumer-centric financial system. As these trends continue to evolve and mature, they promise to democratize access to financial services, reduce costs, and create new opportunities for economic growth and financial inclusion. For consumers, this transformation means greater convenience, better financial products, and more control over their financial data. For businesses, it opens up new revenue streams and opportunities to serve customers more effectively. The success stories emerging from markets like India, Brazil, and Europe demonstrate the tremendous potential of these technologies when supported by appropriate regulatory frameworks and robust digital infrastructure. The future of finance is indeed open, embedded, and more connected than ever before, creating exciting possibilities for all participants in this evolving financial landscape.




Comments