Next Generation GST Reforms in India: A Complete Guide to GST 2.0 Revolution
- Editor

- Sep 5
- 5 min read
by KarNivesh | 05 September, 2025
On September 3, 2025, India saw one of the biggest changes to its tax system since the introduction of GST in 2017. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the launch of GST 2.0, also called the Next Generation GST Reforms. This new system has been described as a “Historic Diwali Gift for the Nation”, as it promises to simplify taxes, reduce prices of daily goods, and give relief to households, farmers, and businesses.
The main goal of GST 2.0 is to move away from the confusing four-slab tax structure and replace it with a simpler, more efficient system that boosts growth and makes life easier for both citizens and businesses.
What is GST 2.0?
GST 2.0 is not just a small tweak but a complete overhaul of India’s indirect tax system. The government has focused on three big pillars:
Structural Reforms – fixing problems like inverted duty structures and long-standing disputes.
Rate Rationalization – reducing the number of tax slabs and putting items in fairer categories.
Ease of Living – making compliance easier with technology, quick refunds, and smoother registration.
The New Slab System
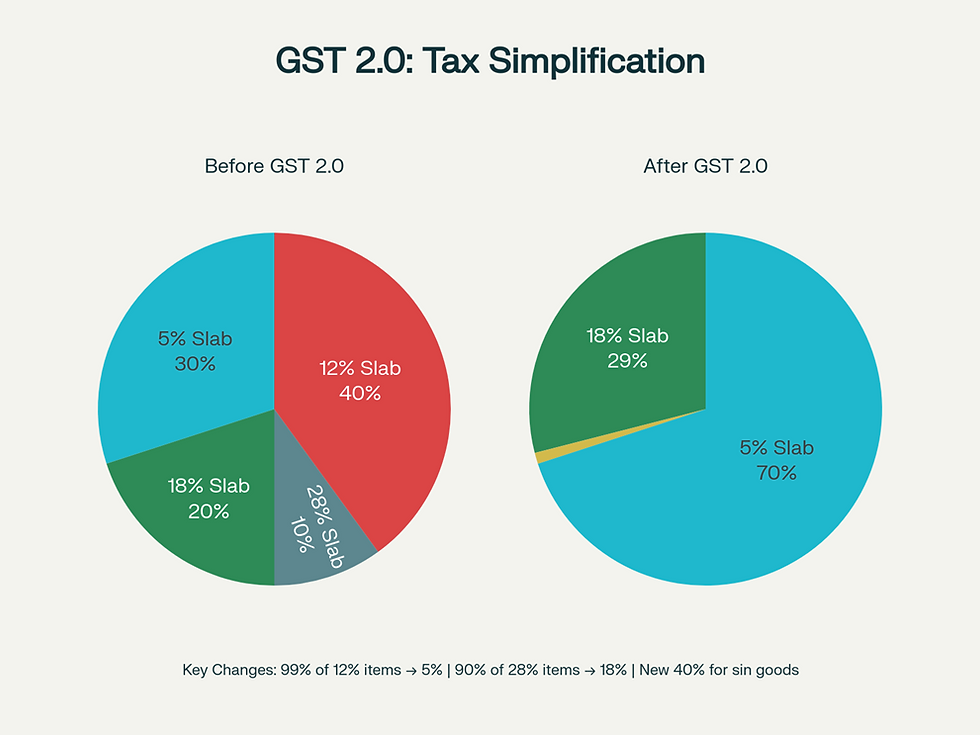
Earlier, GST had four main slabs: 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. These often created confusion and disputes. Under GST 2.0, this has been simplified into three clear categories:
5% Merit Rate – for essential goods and services.
18% Standard Rate – for most items in the economy.
40% Demerit Rate – for luxury and harmful goods.
This change means that 99% of items from the 12% slab have moved to 5%, and 90% of items from the 28% slab have moved to 18%. The result? Greater simplicity and fairness.

How GST 2.0 Helps Daily Life
1. Essentials Become Cheaper
Families will feel the biggest relief in their monthly budgets:
Personal care items like shampoo, toothpaste, hair oil, soap, and toothbrushes are now taxed at just 5% instead of 18%.
Food products like butter, ghee, cheese, namkeen, bhujia, and packaged foods have dropped from 12–18% to just 5%.
Milk, paneer, and Indian breads are now completely tax-free.
Household goods like utensils, kitchenware, napkins, sewing machines, and baby bottles are down to 5% from 12%.
2. Healthcare Gets a Big Boost
Health and life insurance are now fully tax-free (earlier 18%), making them affordable for families, especially senior citizens.
33 critical medicines have moved from 12% GST to 0%, and three cancer/rare-disease drugs from 5% to 0%.
All other medicines now carry just 5% GST instead of 12%.
Medical devices like thermometers, corrective glasses, oxygen, and diagnostic kits have been reduced to 5% from 18%.
3. Education Made Affordable
Items like maps, notebooks, pencils, sharpeners, and globes are now completely tax-free, directly helping students and schools.

Sector-Wise Impact
Agriculture and Rural Economy
Farm equipment like tractors, tyres, irrigation systems, and forestry tools now attract only 5% GST.
Fertilizers and pesticides also see reduced taxes, helping lower input costs.
Bicycles and rural industry equipment are taxed at just 5%, directly supporting rural households.
Automobile Industry
Cars (petrol, diesel, and hybrid) have dropped from 28% to 18%, making them more affordable.
Two-wheelers, buses, trucks, and ambulances are now taxed at 18%.
Auto parts now have a flat 18% rate, ending disputes and making pricing predictable.
Electronics and Appliances
Home appliances like ACs, refrigerators, washing machines, TVs, and dishwashers have moved from 28% to 18%, with prices expected to fall by ₹1,500–₹2,500 per unit.
Tech products like monitors, projectors, and set-top boxes are also now under 18%.
Economic Impact
Growth and Consumption
Experts predict that GST 2.0 will boost India’s GDP by 0.5–1.2% in FY 2026.
Household spending power could rise by about 0.7–0.8% of GDP, giving a major push to consumption.
Inflation could reduce by 0.5–1.1%, if businesses pass on the tax benefits to consumers.
Revenue and Fiscal Balance
The government expects a revenue loss of ₹48,000 crore annually, much lower than earlier fears of ₹1.2 lakh crore.
Higher consumption, better compliance, and reduced tax evasion are expected to make up for this shortfall.
States have been assured of compensation to protect their revenues.
Stock Market and Investment
The markets responded positively: Sensex jumped 900 points and Nifty rose 1% after the announcement.
Sectors like automobiles, FMCG, and consumer durables saw the biggest gains.
Analysts compare this reform’s impact to the 2019 corporate tax cut rally, expecting long-term benefits for consumption-driven industries.
Administrative Reforms
GST 2.0 is not only about tax rates but also about making the system simpler:
Quick Registration – Low-risk businesses can now register within 3 days.
Pre-filled Returns – GSTR forms will be auto-populated to avoid errors.
Faster Refunds – Exporters and manufacturers will get 90% provisional refunds automatically.
Digital Fraud Prevention – AI-based fraud detection, stronger e-invoicing, and even blockchain pilots for invoice tracking are being introduced.
MSME Support – 63 million small businesses will benefit from reduced compliance costs, better cash flow, and fairer tax rules.

Implementation Timeline
Launch Date: September 22, 2025 (just before Navratri, to boost festive demand).
Exceptions: Tobacco will continue under the old GST plus cess until loans are repaid.
Smooth Transition: E-way bills and goods in transit will remain valid to avoid disruption.
Challenges and Safeguards
Revenue loss concerns remain, but the Centre and states reached consensus in a 10.5-hour GST Council meeting.
Businesses will need to update IT systems, invoices, and pricing structures quickly.
The government will monitor to ensure tax cuts are passed on to consumers and not kept as extra profits.
Looking Ahead
GST 2.0 is seen as a stepping stone toward a future single-rate GST (one standard rate plus sin tax), similar to countries like Australia and New Zealand. The next big steps may include bringing petroleum and real estate under GST.
In the long run, GST 2.0 is expected to:
Strengthen India’s domestic consumption model.
Encourage more informal businesses to join the formal economy.
Improve manufacturing competitiveness and export growth.
Conclusion
The Next Generation GST Reforms (GST 2.0) mark a turning point in India’s economic journey. They bring direct benefits for citizens (cheaper essentials, tax-free insurance, and education materials), for farmers (lower input costs), and for businesses (simpler compliance, especially for MSMEs).
The reforms are expected to boost GDP, reduce inflation, and increase competitiveness, while also strengthening household spending power. At the same time, India is better prepared to face global challenges, such as the impact of high US tariffs, by stimulating its own domestic economy.
As Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman emphasized, GST 2.0 ensures stability, predictability, and modernization of India’s tax system. It is more than just a tax reform—it is a roadmap toward a stronger, fairer, and more competitive Indian economy.




Comments